Innovations in Remote Patient Monitoring: Transforming Healthcare Beyond the Clinic
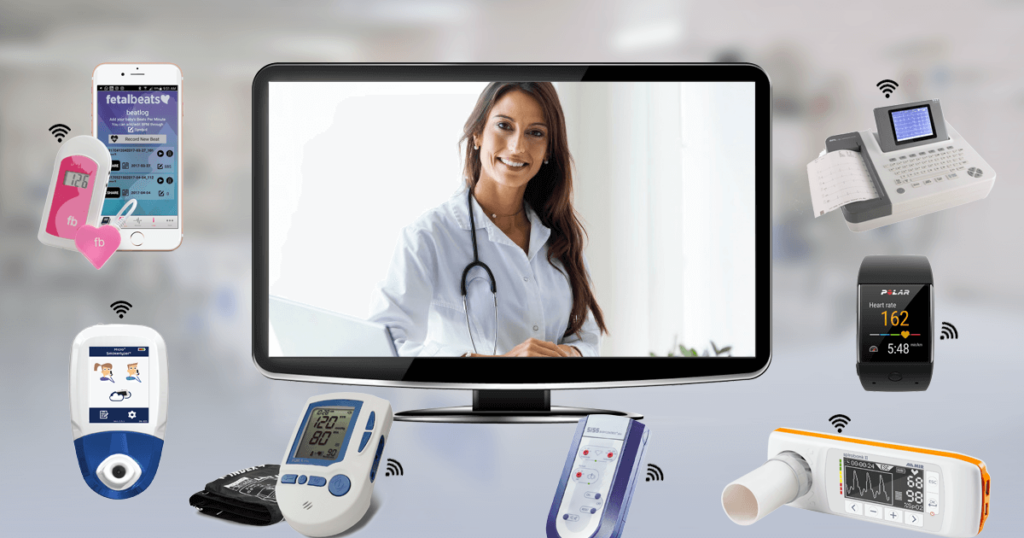

In the rapidly evolving landscape of healthcare, the paradigm shift towards patient-centric care is steering the industry towards innovative solutions. Among these, one standout revolution is the advent of Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM). This transformative approach to healthcare delivery goes beyond the traditional clinic setting, leveraging cutting-edge technologies to monitor patients in the comfort of their homes. This article explores the profound impact of RPM on healthcare, delving into the technologies, benefits, challenges, and the future trajectory of this groundbreaking innovation.
I. Understanding Remote Patient Monitoring
A. The Technological Foundation
- Wearable Devices and Sensors:
- Description: At the core of RPM are wearable devices equipped with sensors that capture a myriad of health metrics. From heart rate and blood pressure to sleep patterns and activity levels, these devices provide real-time data crucial for continuous monitoring.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Integration:
- Description: IoT plays a pivotal role in RPM by facilitating seamless communication between devices and healthcare systems. This interconnected network enables the secure transmission of patient data, ensuring healthcare providers receive timely and accurate information.
II. The Benefits of Remote Patient Monitoring
A. Empowering Patients
- Enhanced Patient Engagement:
- Description: RPM fosters a proactive approach to healthcare, empowering patients to actively participate in their well-being. Real-time access to personal health data encourages individuals to make informed lifestyle choices and adhere to prescribed treatments.
- Improved Chronic Disease Management:
- Description: For patients with chronic conditions, RPM offers continuous monitoring and early detection of fluctuations. This proactive approach not only enhances disease management but also reduces hospitalizations and emergency room visits.
B. Advantages for Healthcare Providers
- Timely Intervention and Prevention:
- Description: Healthcare professionals benefit from RPM by receiving instant alerts for abnormal health readings. This enables timely intervention, preventing complications and reducing the strain on emergency healthcare services.
- Optimized Resource Allocation:
- Description: By remotely monitoring patients, healthcare providers can optimize resource allocation. This means that healthcare facilities can prioritize care for patients who require immediate attention while still providing quality care to those under remote monitoring.
III. Challenges and Considerations
A. Technological Hurdles
- Data Security and Privacy Concerns:
- Description: The influx of patient data from RPM raises concerns about data security and privacy. Striking a balance between accessibility for healthcare providers and ensuring the confidentiality of sensitive health information is a critical challenge.
- Integration with Existing Healthcare Systems:
- Description: Seamless integration of RPM into existing healthcare systems is a complex undertaking. Compatibility issues, standardization of data formats, and interoperability between various technologies pose significant challenges.
B. Regulatory Frameworks
- Compliance with Healthcare Regulations:
- Description: As RPM becomes more widespread, adhering to existing healthcare regulations and ensuring compliance with evolving standards is paramount. Striking the right balance between innovation and regulatory requirements is an ongoing challenge.
- Reimbursement Policies:
- Description: The establishment of clear reimbursement policies for RPM services is crucial for its widespread adoption. Ensuring that healthcare providers are adequately compensated for remote monitoring services is essential for the sustainability of this innovative approach.
IV. The Future Trajectory of Remote Patient Monitoring
A. Technological Advancements
- Artificial Intelligence in RPM:
- Description: The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) holds immense potential for the future of RPM. AI algorithms can analyze vast datasets to identify patterns, predict health trends, and provide personalized insights for both patients and healthcare providers.
- Blockchain for Secure Health Data Management:
- Description: Blockchain technology may address concerns related to data security and privacy. By providing a decentralized and tamper-proof ledger, blockchain can enhance the security and integrity of patient health records in RPM.
B. Telemedicine Synergy
- Collaboration with Telemedicine Platforms:
- Description: The synergy between RPM and telemedicine platforms is anticipated to grow. Combining remote monitoring with virtual consultations creates a comprehensive healthcare ecosystem that offers both continuous monitoring and immediate medical advice.
- Expansion of Remote Diagnostic Capabilities:
- Description: Future iterations of RPM may include advanced diagnostic capabilities. From remote blood tests to at-home diagnostic devices, expanding the scope of remote diagnostics will further enhance the efficacy of RPM in delivering comprehensive healthcare.
V. Conclusion
“Innovations in Remote Patient Monitoring: Transforming Healthcare Beyond the Clinic” signifies a paradigm shift in healthcare delivery, emphasizing a proactive and patient-centric approach. As technology continues to advance, the seamless integration of RPM into mainstream healthcare is on the horizon. By overcoming challenges related to data security, privacy, and regulatory frameworks, RPM stands poised to revolutionize healthcare, providing personalized and continuous monitoring that transcends the boundaries of traditional clinical settings. As we navigate this transformative journey, the collective goal is to build a healthcare landscape that is not only technologically advanced but, more importantly, deeply compassionate and patient-focused.