Preventing Automatic Restarts: A Comprehensive Guide to Disabling Automatic Restart on System Failure in Windows XP
In the world of computing, unexpected system crashes can be a frustrating experience, potentially resulting in data loss, disrupted workflows, and system instability. Windows XP, like its successors, is equipped with a feature called Automatic Restart on System Failure, designed to automatically reboot the system after a critical system error or crash. While this feature aims to ensure system stability and recoverability, it can sometimes hinder troubleshooting efforts by preventing users from viewing error messages or diagnostic information. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve deep into the intricacies of disabling Automatic Restart on System Failure in Windows XP, empowering users to take control of their system’s behavior and facilitate more effective troubleshooting processes.
Understanding Automatic Restart on System Failure:
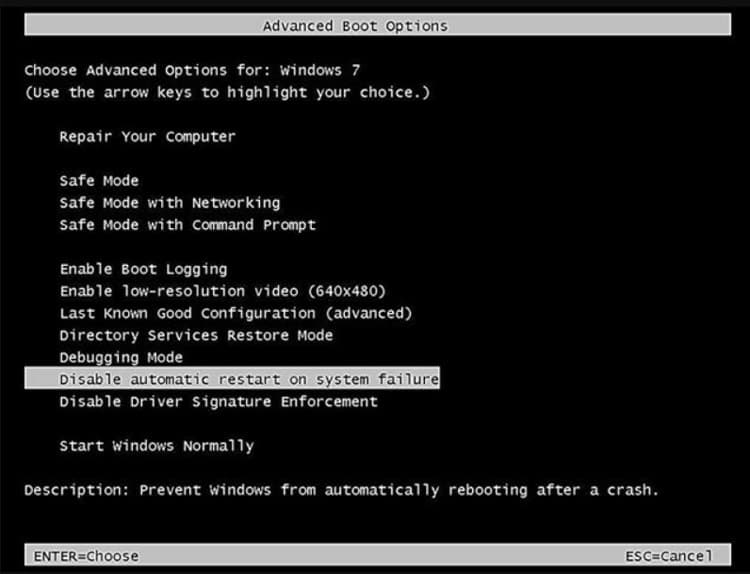
Before we explore the methods for disabling Automatic Restart on System Failure, it’s essential to understand the purpose and implications of this feature within the Windows XP operating system. Automatic Restart on System Failure is a built-in mechanism that automatically reboots the system after encountering a critical system error, commonly known as the “Blue Screen of Death” (BSOD). The rationale behind this feature is to prevent the system from becoming unresponsive or stuck in an unrecoverable state, thereby ensuring system availability and recoverability. However, automatic reboots can sometimes occur too quickly, preventing users from reading error messages or accessing diagnostic information, which can impede troubleshooting efforts and prolong downtime.
Step-by-Step Guide to Disabling Automatic Restart on System Failure:
Now, let’s explore a systematic approach to disabling Automatic Restart on System Failure in Windows XP:
Step 1: Accessing System Properties:
- Click on the “Start” button located at the bottom-left corner of the screen.
- Right-click on the “My Computer” icon and select “Properties” from the context menu.
- Alternatively, you can press the “Windows” key + “Pause/Break” key combination to access System Properties directly.
Step 2: Accessing Advanced System Settings:
- In the System Properties window, navigate to the “Advanced” tab.
- Under the “Advanced” tab, locate and click on the “Settings” button under the “Startup and Recovery” section.
Step 3: Modifying Startup and Recovery Settings:
- In the Startup and Recovery window, locate the “System failure” section.
- Uncheck the box next to “Automatically restart” to disable Automatic Restart on System Failure.
- Optionally, you can adjust other settings such as writing an event to the system log or creating a memory dump file for diagnostic purposes.
- Click “OK” to save the changes and close the Startup and Recovery window.
- Click “OK” again to save the changes and close the System Properties window.
Using Registry Editor (Advanced Method):
For advanced users or those who prefer using the Registry Editor, Windows XP offers the option to disable Automatic Restart on System Failure through registry modifications:
- Press the “Windows” key + “R” key combination to open the Run dialog box.
- Type “regedit” and press Enter to open the Registry Editor.
- Navigate to the following registry key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\CrashControl - In the right pane, double-click on the “AutoReboot” value.
- Change the value data from “1” to “0” to disable Automatic Restart on System Failure.
- Click “OK” to save the changes and close the Registry Editor.
Important Considerations:
Before disabling Automatic Restart on System Failure, consider the following important considerations:
- Impact on System Stability: Disabling Automatic Restart on System Failure may expose the system to prolonged periods of unresponsiveness in the event of a critical system error. Ensure that you understand the potential impact on system stability and availability before making changes.
- Troubleshooting Benefits: Disabling Automatic Restart on System Failure allows users to read error messages and access diagnostic information more effectively, facilitating faster and more accurate troubleshooting processes.
- Reverting Changes: If necessary, you can revert the changes and re-enable Automatic Restart on System Failure by following the same steps outlined above and rechecking the box next to “Automatically restart.”
Conclusion:
In conclusion, disabling Automatic Restart on System Failure in Windows XP is a proactive measure that empowers users to take control of their system’s behavior and facilitate more effective troubleshooting processes in the event of a critical system error. By following the step-by-step guide outlined in this article and considering important considerations, users can disable Automatic Restart on System Failure with confidence and precision, ensuring improved access to error messages and diagnostic information. Whether troubleshooting system errors, analyzing BSOD occurrences, or optimizing system stability, mastering the management of Automatic Restart on System Failure enhances the overall reliability and recoverability of your Windows XP system. So take control of your system’s behavior today, disable Automatic Restart on System Failure, and empower yourself to overcome unexpected system challenges with ease.