Mastering Image Enhancement: A Comprehensive Guide to Auto Tone, Auto Contrast, and Auto Color in Photoshop
Introduction:
Adobe Photoshop stands as the unparalleled powerhouse in the realm of image editing, providing a plethora of tools and features to transform and enhance photographs. Among the arsenal of tools at the disposal of Photoshop users, the trio of Auto Tone, Auto Contrast, and Auto Color holds a special place. In this extensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of these automated image adjustment tools, exploring how they work, when to use them, and how they contribute to streamlining the image enhancement process.
Understanding Auto Tone, Auto Contrast, and Auto Color:
- Auto Tone:
- Auto Tone in Photoshop is designed to automatically adjust the tonal range of an image, optimizing the distribution of brightness and contrast. This adjustment aims to enhance the overall tonal balance, ensuring that the image’s highlights, shadows, and midtones are well-distributed. Auto Tone can be particularly useful in correcting exposure issues, making it an excellent starting point for further manual adjustments.
- Auto Contrast:
- Auto Contrast, as the name suggests, automatically adjusts the contrast of an image. It works by identifying the lightest and darkest pixels in an image and stretching the tonal range to ensure that these extremes are fully utilized. This results in a more dynamic and visually appealing contrast. Auto Contrast is beneficial for images that may appear flat or lack punch, providing a quick enhancement to the overall visual impact.
- Auto Color:
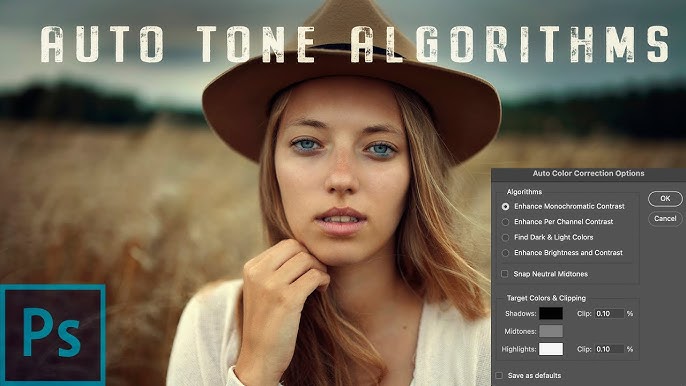
- Auto Color is focused on automatically adjusting the color balance of an image. This tool aims to correct any color cast present in the image by analyzing the overall color distribution and making adjustments to achieve a more neutral and balanced appearance. Auto Color can be particularly useful for correcting white balance issues and ensuring that the colors in the image are true to life.
When to Use Auto Tone, Auto Contrast, and Auto Color:
- Quick Fixes and Batch Processing:
- Auto Tone, Auto Contrast, and Auto Color are invaluable when working with a large number of images that require quick adjustments. For instance, when dealing with a batch of photos taken in similar lighting conditions, applying these automated adjustments can save time and provide a consistent look across the entire set.
- Starting Points for Manual Refinement:
- These automated tools serve as excellent starting points for more intricate manual adjustments. After applying Auto Tone, Auto Contrast, or Auto Color, users can fine-tune specific elements using other Photoshop tools, such as Levels, Curves, or Color Balance, to achieve a customized and precise result.
- Correcting Exposure and Color Cast Issues:
- Auto Tone and Auto Color are particularly useful for correcting exposure and color balance issues in images. When faced with underexposed or overexposed photographs, applying Auto Tone can quickly rectify exposure problems. Similarly, Auto Color is effective in eliminating unwanted color casts caused by varying light sources.
- Streamlining Workflows:
- These automated adjustments are powerful tools for streamlining workflows, especially when time is of the essence. They provide a rapid means of achieving initial corrections, allowing users to focus on more intricate aspects of image editing.
In-Depth Usage Tips and Techniques:
- Selective Application:
- Auto Tone, Auto Contrast, and Auto Color can be selectively applied to specific layers or areas within an image using adjustment layers or masks. This allows users to target adjustments only to the areas that require enhancement while preserving the integrity of other elements.
- Adjustment Layer Approach:
- Leveraging adjustment layers for Auto Tone, Auto Contrast, and Auto Color provides a non-destructive workflow. By applying these adjustments as separate layers, users can easily toggle their effects on and off, compare results, and make further adjustments without altering the original image data.
- Fine-Tuning with Manual Adjustments:
- While the automated tools are powerful, they may not always produce the desired result on their own. Combining Auto Tone, Auto Contrast, or Auto Color with manual adjustments allows for a more nuanced and customized approach to image enhancement. For example, using the Curves adjustment layer to refine tonal values after applying Auto Tone.
- Setting Default Behaviors:
- Photoshop allows users to customize the default behaviors of Auto Tone, Auto Contrast, and Auto Color. By accessing the Preferences menu, users can define the parameters and settings that align with their preferred editing style, ensuring a more personalized and efficient workflow.
Conclusion:
Auto Tone, Auto Contrast, and Auto Color in Adobe Photoshop represent indispensable tools in the image editing arsenal, offering efficiency and convenience without sacrificing quality. Whether used as a quick fix for batch processing or as a starting point for more intricate adjustments, these automated tools streamline workflows and provide a solid foundation for image enhancement. By understanding their functionalities, knowing when to apply them, and employing complementary manual adjustments, users can harness the full potential of Auto Tone, Auto Contrast, and Auto Color to achieve stunning and visually captivating results in their photographs.