Mastering Remote Assistance: A Comprehensive Guide to Using Windows Remote Assistance in Windows 7
In the interconnected world of computing, remote assistance tools play a crucial role in facilitating collaboration, troubleshooting, and support across geographically dispersed environments. Windows Remote Assistance, a built-in feature of Windows 7, empowers users to seek and provide assistance remotely, enabling seamless communication and problem-solving. In this exhaustive guide, we will embark on a journey to demystify the process of using Windows Remote Assistance in Windows 7, exploring its intricacies and providing step-by-step instructions for leveraging its capabilities to support and troubleshoot remote users.
Understanding Windows Remote Assistance in Windows 7:
Before delving into the intricacies of using Windows Remote Assistance, let’s first grasp the concept and significance of this indispensable tool:
- Definition: Windows Remote Assistance is a collaborative support tool integrated into Windows 7 that allows users to request and provide assistance to others remotely over the internet or a local network.
- Real-Time Interaction: Windows Remote Assistance enables real-time interaction between the helper and the recipient, allowing for screen sharing, mouse and keyboard control, file transfer, and chat communication.
- Security and Privacy: Windows Remote Assistance employs encryption and authentication mechanisms to ensure the security and privacy of remote sessions, protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access.
Using Windows Remote Assistance in Windows 7:
Now, let’s explore the step-by-step process of using Windows Remote Assistance to provide and receive assistance in Windows 7:
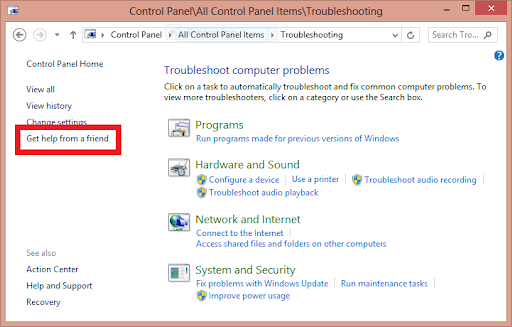
- Accessing Windows Remote Assistance:
- Click on the Start button in the taskbar.
- Navigate to “All Programs” > “Maintenance” > “Windows Remote Assistance.”
- Choosing Assistance Option:
- In the Windows Remote Assistance window, select whether you want to offer assistance or request assistance.
- If offering assistance, choose “Invite someone you trust to help you” and follow the prompts to generate an invitation file.
- Generating Invitation File:
- Specify the method for sending the invitation, such as email or a saved file.
- Customize the invitation with a message and set an expiration date for the invitation file.
- Sending Invitation:
- Send the invitation file to the person you want to assist via the selected method.
- Ensure that the recipient receives the invitation and follows the instructions to initiate the remote assistance session.
- Initiating Remote Assistance:
- If receiving assistance, open the invitation file received from the helper.
- Follow the prompts to accept the invitation and initiate the remote assistance session.
- Collaborating Remotely:
- Once the remote assistance session is established, the helper gains control of the recipient’s computer and can perform various tasks, such as troubleshooting issues, configuring settings, and demonstrating procedures.
- The recipient can observe the helper’s actions, communicate via chat, and regain control of their computer at any time.
Advanced Features and Tips:
To further enhance the remote assistance experience and optimize collaboration in Windows 7, consider the following advanced features and tips:
- Customizing Remote Assistance Settings:
- Explore the settings and options in Windows Remote Assistance to customize session preferences, such as screen sharing quality, control level, and security settings.
- Adjust settings to optimize performance, privacy, and security based on your requirements and preferences.
- Using Group Policy for Centralized Management:
- Organizations and IT administrators can leverage Group Policy settings to configure and manage Windows Remote Assistance settings centrally across multiple computers and users.
- Customize Group Policy settings to enforce security policies, control access permissions, and streamline remote assistance workflows.
- Troubleshooting Connection Issues:
- If encountering connection issues during a remote assistance session, troubleshoot network connectivity, firewall settings, and other potential barriers to communication.
- Ensure that both the helper and the recipient have stable internet connections and proper network configurations to facilitate smooth remote assistance sessions.
- Ensuring Data Security and Privacy:
- Prioritize data security and privacy during remote assistance sessions by adhering to best practices for encryption, authentication, and access control.
- Avoid sharing sensitive information or accessing confidential data unless necessary, and implement additional security measures as needed to protect sensitive information.
Conclusion:
Windows Remote Assistance is a powerful tool that empowers users to collaborate, troubleshoot, and support each other remotely in Windows 7. By following the comprehensive guide outlined above, users can harness the capabilities of Windows Remote Assistance to provide and receive assistance effectively, streamline troubleshooting workflows, and enhance productivity. Whether it’s resolving technical issues, demonstrating procedures, or offering guidance, Windows Remote Assistance provides users with the tools and flexibility to support and assist others remotely with confidence. So embrace the power of remote collaboration today, leverage Windows Remote Assistance with ease, and unlock new possibilities for support and assistance in Windows 7.