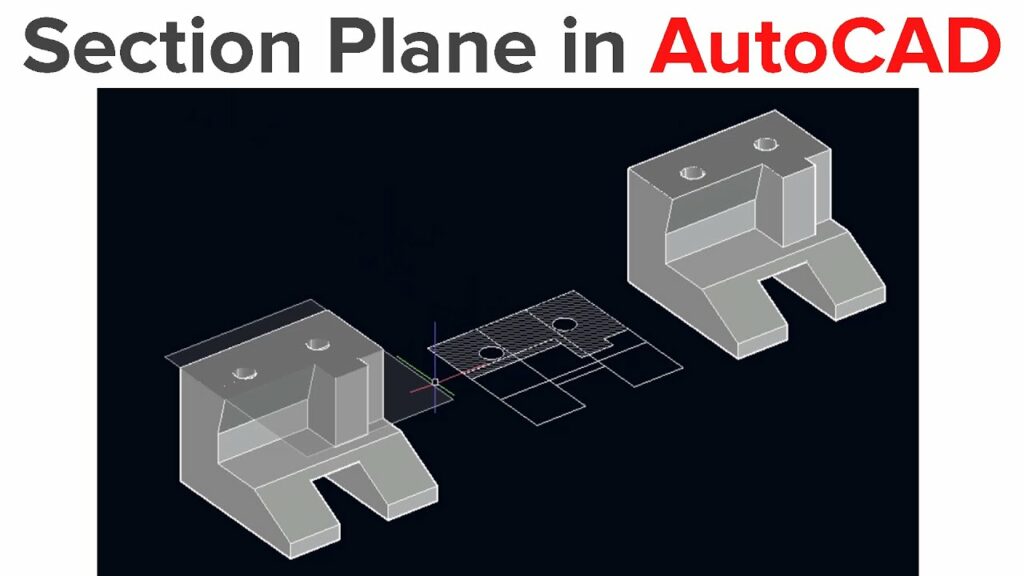
Navigating the Depths: A Comprehensive Exploration of the Section Plane Command in AutoCAD
Introduction:
In the intricate world of computer-aided design (CAD), AutoCAD stands as a cornerstone, empowering designers to bring their visions to life. Among the plethora of tools and commands that AutoCAD offers, the Section Plane command emerges as a powerful feature, allowing designers to dissect three-dimensional models and gain unparalleled insights into their internal structures. This comprehensive article embarks on a detailed exploration of the Section Plane command in AutoCAD, unraveling its functionalities, applications, customization options, and the transformative impact it has on the design process.
I. Understanding the Section Plane Command:
- Definition and Functionality: The Section Plane command in AutoCAD is a tool designed to cut through three-dimensional models, revealing cross-sectional views of objects or spaces. By creating a virtual plane within the model, designers can visualize and analyze internal details, facilitating a deeper understanding of complex structures.
- Significance in 3D Modeling: The Section Plane command is particularly significant in the realm of 3D modeling, where the visualization of internal components is crucial. It enhances the ability to assess spatial relationships, identify design flaws, and communicate intricate details in a comprehensive manner.
II. Utilizing the Section Plane Command:
- Activation and Placement: Activating the Section Plane command involves navigating the AutoCAD ribbon or typing relevant commands. Once activated, designers can place the section plane within the model at a specific location and orientation, aligning it with the desired cutting plane.
- Adjusting Parameters: The Section Plane command allows for the adjustment of parameters such as the cutting depth, rotation, and display options. Designers can customize these parameters to create precise cross-sections tailored to their specific visualization needs.
III. Applications in Design and Analysis:
- Architectural Visualization: In architectural design, the Section Plane command proves invaluable for showcasing interior spaces, revealing structural elements, and providing clients with a realistic preview of the building’s internal layout. It aids in the evaluation of spatial relationships and lighting conditions.
- Mechanical Engineering: Within the realm of mechanical engineering, the Section Plane command facilitates the examination of intricate assemblies and components. Designers can analyze the internal workings of machinery, identify interferences, and optimize designs for functionality and manufacturability.
IV. Customization Options:
- Display Styles: AutoCAD offers various display styles for section planes, allowing designers to choose between wireframe, hidden line, and realistic views. These options enhance the visual representation of cross-sections, catering to different preferences and presentation requirements.
- Hatching and Fills: The Section Plane command enables the application of hatching or fills to the cut surfaces, enhancing the clarity of cross-sectional views. Designers can customize the appearance of the section cut, distinguishing between different materials or components within the model.
V. Section Plane Visibility and Interaction:
- Visibility Controls: AutoCAD provides controls for toggling the visibility of section planes, allowing designers to seamlessly switch between full 3D views and cross-sectional perspectives. This feature enhances the flexibility of design exploration and presentation.
- Interactivity and Dynamic Updates: The Section Plane command in AutoCAD is dynamic, providing real-time updates as the model is modified. Designers can interactively adjust the section plane’s position or orientation, witnessing instant changes in the cross-sectional view.
VI. Annotation and Documentation:
- Dimensioning and Labeling: The Section Plane command facilitates the addition of dimensions and labels to the cross-sectional views. Designers can annotate critical dimensions, materials, or components, creating comprehensive documentation for internal and external stakeholders.
- Exporting Section Views: Cross-sectional views generated with the Section Plane command can be exported as separate drawings or included in project documentation. This capability streamlines the creation of detailed design documentation for presentations, reports, or collaboration purposes.
VII. Troubleshooting and Best Practices:
- Handling Section Plane Issues: Designers may encounter challenges related to the Section Plane command, such as unexpected behavior or display anomalies. Troubleshooting tips, including verifying model integrity and adjusting settings, can aid in resolving issues and ensuring smooth functionality.
- Best Practices for Efficient Usage: Implementing best practices enhances the efficiency of using the Section Plane command. These practices include organizing models with layers, strategically placing section planes, and utilizing visualization settings to achieve optimal results.
VIII. Collaborative Workflows and Section Plane:
- Collaborative Design Reviews: The Section Plane command facilitates collaborative design reviews by allowing multiple stakeholders to explore and discuss internal details of a model. This collaborative approach enhances communication and ensures that all team members have a comprehensive understanding of the design.
- Interdisciplinary Collaboration: In interdisciplinary projects involving architects, engineers, and other professionals, the Section Plane command becomes a tool for effective communication. It enables each discipline to focus on specific aspects of the design, fostering a holistic and integrated approach to project development.
IX. Future Developments and Emerging Trends:
- Augmented Reality Integration: The integration of augmented reality (AR) technologies may redefine the Section Plane command’s role. Visualizing cross-sectional views in real-world environments through AR could revolutionize design reviews, allowing users to interact with 3D models in physical spaces.
- Enhancements in Visualization: As AutoCAD evolves, enhancements in visualization capabilities may impact the Section Plane command. Advanced rendering techniques, improved lighting simulations, and virtual reality integration could elevate the tool’s capacity for delivering immersive and realistic cross-sectional experiences.
Conclusion:
In the expansive landscape of AutoCAD, the Section Plane command emerges as a beacon, guiding designers through the intricate layers of three-dimensional models. Its transformative capabilities in visualization, analysis, and communication elevate the design process, enabling a deeper understanding of complex structures. This comprehensive exploration has navigated the intricacies of the Section Plane command, shedding light on its functionalities, customization options, applications across diverse industries, and its evolving role in the future of computer-aided design. As AutoCAD continues to be at the forefront of innovation, the Section Plane command remains an indispensable tool, unlocking new dimensions of creativity and insight for designers worldwide.