Windows Task Scheduler is a powerful built-in tool in Windows 8 that allows users to automate various tasks, such as running programs, scripts, or batch files, at scheduled times or in response to specific events. Task Scheduler enables users to streamline their workflow, increase productivity, and ensure that important tasks are executed efficiently without manual intervention. Whether it’s performing routine maintenance, launching backup processes, or running system utilities, Task Scheduler provides a flexible and customizable solution for automating repetitive tasks. In this extensive guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about using Windows Task Scheduler in Windows 8, from accessing the tool to creating and managing scheduled tasks effectively.
Understanding Windows Task Scheduler:
Windows Task Scheduler is a system utility that allows users to schedule and automate tasks to be performed at predefined times or in response to specific triggers. It provides a graphical interface for creating, managing, and monitoring scheduled tasks, making it easy for users to automate various processes without the need for complex scripting or programming. Task Scheduler can execute a wide range of actions, including running programs, executing scripts or commands, sending emails, and more, making it a versatile tool for automating routine tasks and optimizing system performance.
Accessing Windows Task Scheduler:
To access Windows Task Scheduler in Windows 8, follow these steps:
- Open Control Panel: Press the Windows key + X to open the Power User menu, then click or tap on “Control Panel.”
- Access Administrative Tools: In the Control Panel, navigate to “System and Security” > “Administrative Tools.”
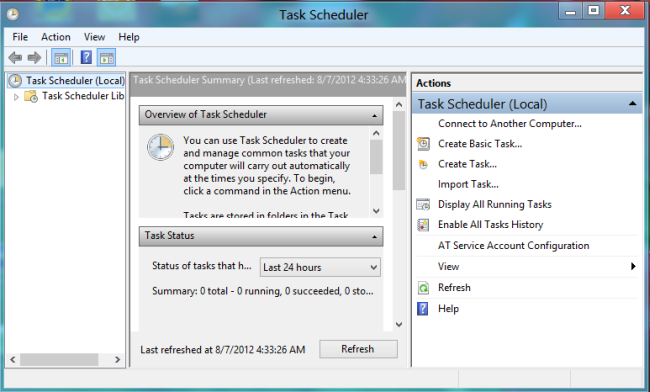
- Open Task Scheduler: In the Administrative Tools window, double-click or tap on “Task Scheduler” to launch the Task Scheduler application.
Creating a Basic Task:
Once you’ve accessed Task Scheduler, follow these steps to create a basic scheduled task:
- Navigate to Task Scheduler Library: In the Task Scheduler window, click or tap on “Task Scheduler Library” in the left pane to view existing tasks or create a new task.
- Create New Task: In the Actions pane on the right side of the Task Scheduler window, click or tap on “Create Basic Task” to launch the Create Basic Task Wizard.
- Name and Description: Enter a name and description for the task to help identify it later. Click or tap on “Next” to continue.
- Trigger: Choose a trigger for the task, such as “Daily,” “Weekly,” or “One time.” Follow the prompts to specify the trigger details, such as the start date, time, and recurrence pattern.
- Action: Select the action you want the task to perform, such as “Start a program,” “Send an email,” or “Display a message.” Follow the prompts to specify the action details, such as the program to run or the message to display.
- Finish: Review the task settings and click or tap on “Finish” to create the task. The new task will now appear in the Task Scheduler Library, where you can view and manage it alongside other scheduled tasks.
Advanced Task Configuration:
In addition to creating basic tasks, Task Scheduler also offers advanced options for configuring tasks with more complex requirements. Here are some advanced task configuration options available in Task Scheduler:
- Trigger Conditions: Customize trigger conditions to control when a task should be executed based on criteria such as idle time, user login, or system startup/shutdown.
- Actions: Configure multiple actions for a single task, allowing you to perform a series of actions sequentially or in parallel.
- Conditions: Specify conditions that must be met for the task to run, such as network availability, power status, or system idle time.
- Settings: Adjust task settings, such as priority, compatibility, and security options, to optimize task performance and ensure compatibility with the target environment.
Managing Scheduled Tasks:
Once you’ve created scheduled tasks, Task Scheduler provides tools for managing and monitoring task execution. Here are some common tasks you can perform in Task Scheduler:
- View Task Properties: Double-click or tap on a task in the Task Scheduler Library to view its properties and modify settings, triggers, actions, and conditions.
- Run Task Manually: Right-click on a task and select “Run” to execute the task manually outside of its scheduled time.
- Disable or Delete Task: Right-click on a task and select “Disable” to temporarily disable the task without deleting it. To delete a task, select “Delete.”
- View Task History: Click or tap on “Task Scheduler Library” in the left pane, then click or tap on “View” > “Show Hidden Tasks” to display the History tab. Here, you can view the execution history of scheduled tasks, including success and error messages.
Troubleshooting Task Scheduler Issues:
If you encounter issues with Task Scheduler, such as tasks not running as expected or errors during task execution, here are some troubleshooting steps you can take:
- Check Task Conditions: Verify that the conditions specified for the task are being met, such as trigger conditions, user permissions, and system requirements.
- Review Task History: Check the task history in Task Scheduler to identify any errors or issues that may have occurred during task execution. Look for error messages or status codes that may indicate the cause of the problem.
- Verify Task Actions: Ensure that the actions specified for the task are configured correctly, including program paths, command-line arguments, and required permissions.
- Test Task Manually: Run the task manually from Task Scheduler to verify that it executes correctly outside of its scheduled time. This can help identify any issues with the task configuration or execution environment.
- Check System Resources: Make sure that the system has adequate resources available to execute the task, such as CPU, memory, disk space, and network bandwidth.
Conclusion:
Windows Task Scheduler is a powerful tool for automating tasks and streamlining workflow in Windows 8. By creating and managing scheduled tasks, users can automate routine processes, optimize system performance, and increase productivity. Whether it’s running programs, executing scripts, or sending emails, Task Scheduler provides a flexible and customizable solution for automating a wide range of tasks. By understanding how to use Task Scheduler effectively and following best practices for task configuration and management, users can harness the full potential of this built-in utility and enhance their computing experience in Windows 8.