How to use Windows Firewall in Windows 8
Windows Firewall is a critical component of the Windows operating system, providing essential protection against unauthorized access to your computer from the internet or other networks. It acts as a barrier between your computer and potential threats, monitoring incoming and outgoing network traffic and blocking or allowing connections based on predefined rules. In Windows 8, Windows Firewall offers advanced features and settings to help users customize their network security and protect their computer from various online threats. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about using Windows Firewall in Windows 8, from accessing firewall settings to configuring rules and monitoring network activity effectively.
Understanding Windows Firewall:
Windows Firewall is a software-based firewall that comes pre-installed with Windows operating systems. Its primary function is to filter network traffic based on predefined rules and policies, allowing only authorized connections to access your computer’s resources while blocking unauthorized access attempts. Windows Firewall helps protect your computer from various network-based attacks, including malware infections, hacking attempts, and unauthorized access to sensitive data.
Accessing Windows Firewall Settings:
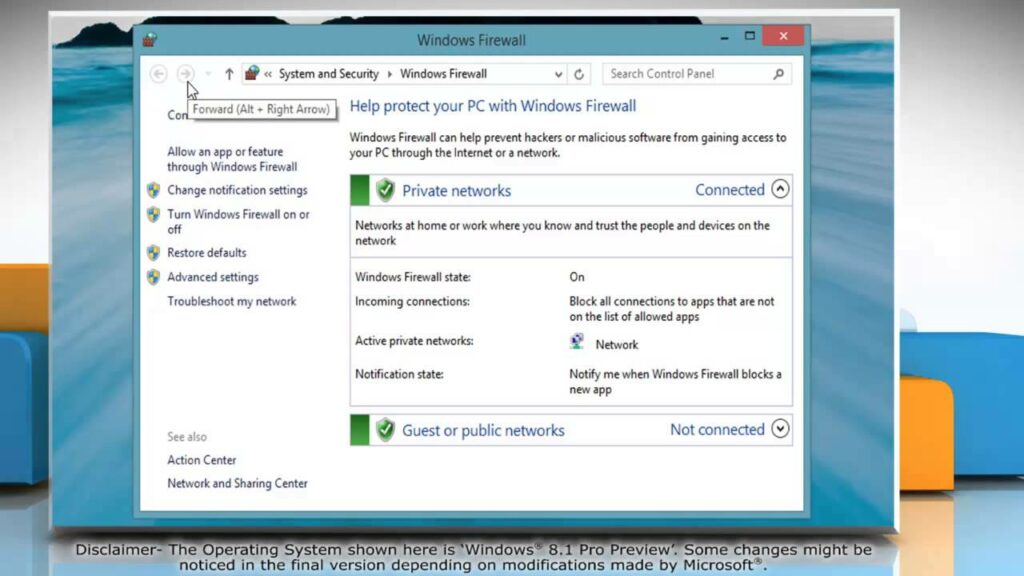
To access Windows Firewall settings in Windows 8, follow these steps:
- Open Control Panel: Press the Windows key + X to open the Power User menu, then click or tap on “Control Panel.”
- Access Windows Firewall: In the Control Panel, navigate to “System and Security” > “Windows Firewall.” This opens the Windows Firewall settings window, where you can configure firewall rules and settings.
Configuring Windows Firewall Rules:
Windows Firewall uses rules to determine how it handles incoming and outgoing network traffic. By creating and configuring firewall rules, you can specify which types of connections are allowed or blocked, as well as define exceptions for specific programs or services. Here’s how to configure Windows Firewall rules:
- Access Advanced Settings: In the Windows Firewall settings window, click or tap on “Advanced settings” in the left pane. This opens the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security console, where you can create and manage firewall rules.
- Create New Rule: To create a new firewall rule, click or tap on “New Rule” in the right pane. This launches the New Inbound Rule Wizard or New Outbound Rule Wizard, depending on whether you want to create an inbound or outbound rule.
- Specify Rule Type: In the wizard, choose the type of rule you want to create, such as a program, port, or predefined rule. Follow the prompts to specify the details of the rule, including the action (allow or block), the program or port to which the rule applies, and any additional conditions or criteria.
- Review Rule Settings: Review the settings of the new rule to ensure that it accurately reflects your intended configuration. You can customize the rule further by editing its properties or adding additional criteria as needed.
- Apply Rule: Once you’re satisfied with the rule settings, click or tap on “Finish” to create the rule and apply it to Windows Firewall. The new rule will now be listed in the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security console, where you can view and manage it alongside other firewall rules.
Monitoring Windows Firewall Activity:
Windows Firewall provides tools for monitoring network activity and viewing firewall logs to track connections and security events. Here’s how to monitor Windows Firewall activity in Windows 8:
- Access Firewall Logs: In the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security console, click or tap on “Monitoring” in the left pane. This opens the Monitoring section, where you can view firewall activity and security logs.
- View Firewall Activity: In the Monitoring section, you can view active firewall rules, connection security rules, and security associations. You can also access firewall logs to view detailed information about network traffic, including allowed and blocked connections, rule matches, and security events.
- Filter and Search Logs: Use the filtering and search options in the firewall logs to narrow down the results and find specific information. You can filter logs based on criteria such as date and time, source and destination IP addresses, protocol type, and action (allow or block).
- Analyze Security Events: Review security events and alerts in the firewall logs to identify potential security threats or suspicious activity. Look for patterns or anomalies in the log data that may indicate unauthorized access attempts, malware infections, or other security incidents.
Troubleshooting Windows Firewall Issues:
If you encounter issues with Windows Firewall, such as connectivity problems or unexpected behavior, there are several troubleshooting steps you can take to resolve the problem:
- Check Firewall Settings: Ensure that Windows Firewall is enabled and configured correctly. Open Windows Firewall settings in the Control Panel or Windows Firewall with Advanced Security console and review the settings and rules to make sure they’re configured as intended.
- Verify Program Exceptions: If you’re experiencing issues with specific programs or services, make sure that they’re allowed through Windows Firewall. Check the list of firewall rules and verify that there are exceptions for the programs or ports used by the affected applications.
- Restart Firewall Service: Sometimes, restarting the Windows Firewall service can resolve connectivity issues or other problems. Open the Services console (services.msc), locate the Windows Firewall service, and restart it. Make sure that the service is set to start automatically.
- Scan for Malware: Run a full system scan with antivirus and antimalware software to check for and remove any malware infections that may be affecting Windows Firewall or network connectivity.
- Reset Firewall Settings: If all else fails, you can reset Windows Firewall to its default settings. Open Windows Firewall settings in the Control Panel, click or tap on “Restore defaults” in the left pane, and then follow the prompts to reset Windows Firewall settings.
Conclusion:
Windows Firewall is a powerful tool for protecting your computer from unauthorized access and network-based threats. By configuring firewall rules, monitoring network activity, and troubleshooting issues effectively, you can ensure that Windows Firewall provides robust security for your Windows 8 computer. Whether you’re a novice user or an advanced administrator, understanding how to use Windows Firewall effectively is essential for maintaining a secure and reliable computing environment. By following the steps outlined in this guide and staying vigilant about network security, you can keep your Windows 8 computer protected from online threats and enjoy peace of mind knowing that your data and privacy are safeguarded.




